Making plots from GHRU data
Anthony Underwood
ploting_GHRU_data.RmdIntroduction
This vignette will demonstrate how to use some of the inbuilt GHRU R functions to plot data
Getting the required data
For these plots we will need epi data, MLST data and AMR data.
library(ghruR)
library(kableExtra)
epi_data <- ghruR::get_data_for_country(
country_value = "India",
type_value = "Epidemiological Metadata",
user_email = "anthony.underwood@cgps.group")## [1] "anthony.underwood@cgps.group"
## [1] "anthony.underwood@cgps.group"
## [1] "anthony.underwood@cgps.group"
epi_data <- ghruR::clean_data(epi_data)
mlst_data <- ghruR::get_data_for_country(
country_value = "India",
type_value = "MLST",
user_email = "anthony.underwood@cgps.group")## [1] "anthony.underwood@cgps.group"
amr_data <- ghruR::get_data_for_country(
country_value = "India",
type_value = "AMR Klebsiella pneumoniae",
AMR_type = "acquired",
user_email = "anthony.underwood@cgps.group")## [1] "anthony.underwood@cgps.group"Basic stats
# Select just the data for which we have AMR data
kpn_ids <- amr_data %>% pull(`Sample id`)
combined_data <- epi_data %>%
dplyr::filter(`Sample id` %in% kpn_ids) %>%
left_join(mlst_data, by = 'Sample id')
# Show some basic stats
samples_per_sentinel_site <- count_samples_by_sentinel_site(combined_data)
samples_per_sentinel_site %>% kable() %>% kable_styling() %>% scroll_box(width = "100%")| Sentinel Site Code | Sample Count |
|---|---|
| AIIMSJ | 19 |
| APH | 5 |
| BCH | 258 |
| BCR | 9 |
| CMC | 8 |
| IGIMS | 21 |
| IPH | 1 |
| JAY | 70 |
| JIP | 55 |
| KGMU | 9 |
| KMC | 28 |
| KMN | 1 |
| LPL | 3 |
| MEDQ | 2 |
| MIMS | 5 |
| NIM | 5 |
| PRIM | 7 |
| RBH | 7 |
| RRM | 13 |
| SDU | 5 |
| SMF | 5 |
| SMS | 7 |
| TSRM | 6 |
| UTK | 29 |
| VPC | 64 |
Plotting ST data
Plot all STs ordered by count
st_counts <- ghruR::count_sts(combined_data)
st_plot <- plot_sts(st_counts, order_by_count = TRUE)
print(st_plot)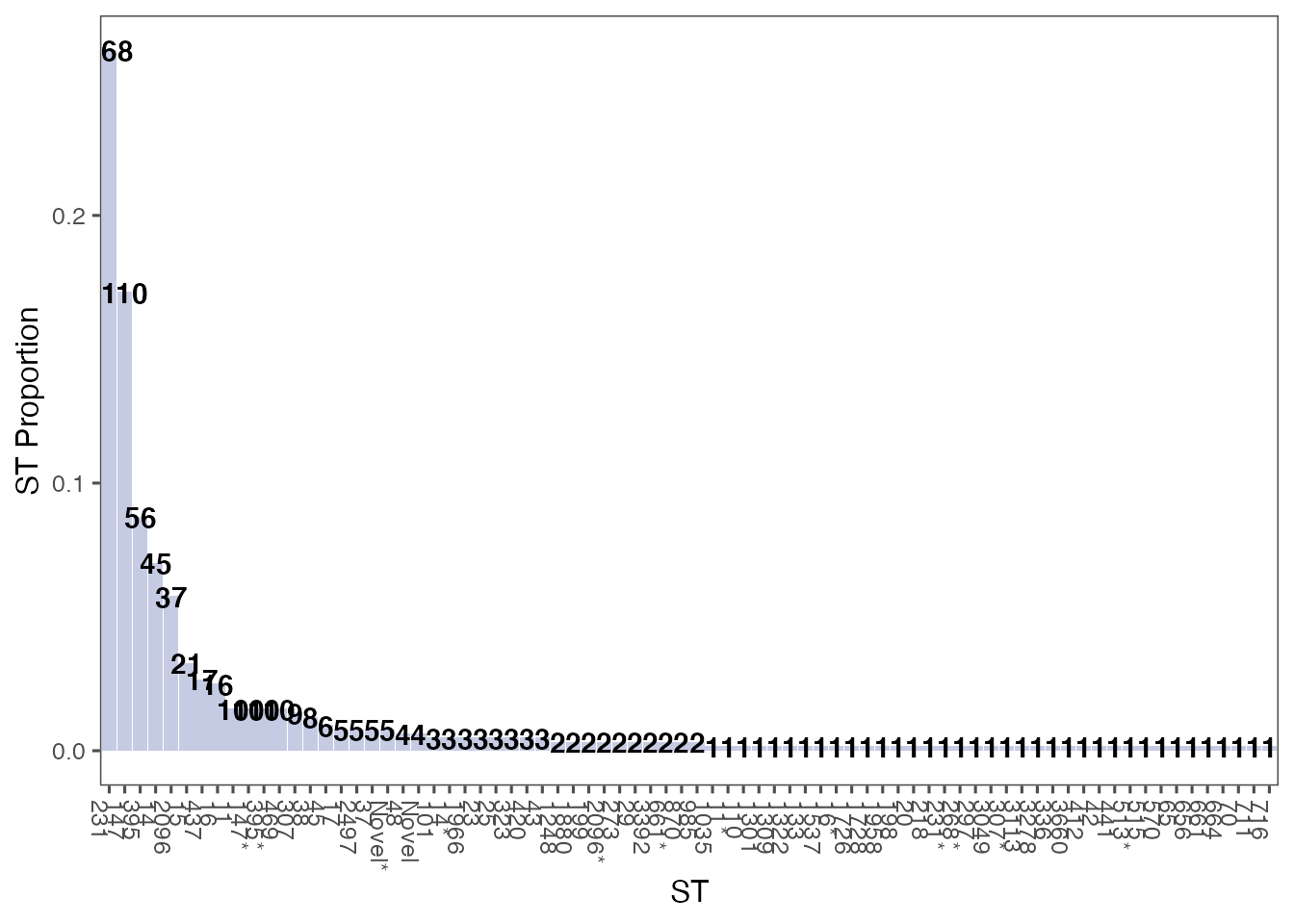
Plot top 10 most frequent STs ordered by count
most_frequent_sts <- count_most_frequent_sts(st_counts)
st_plot <- plot_sts(most_frequent_sts, order_by_count = TRUE)
print(st_plot)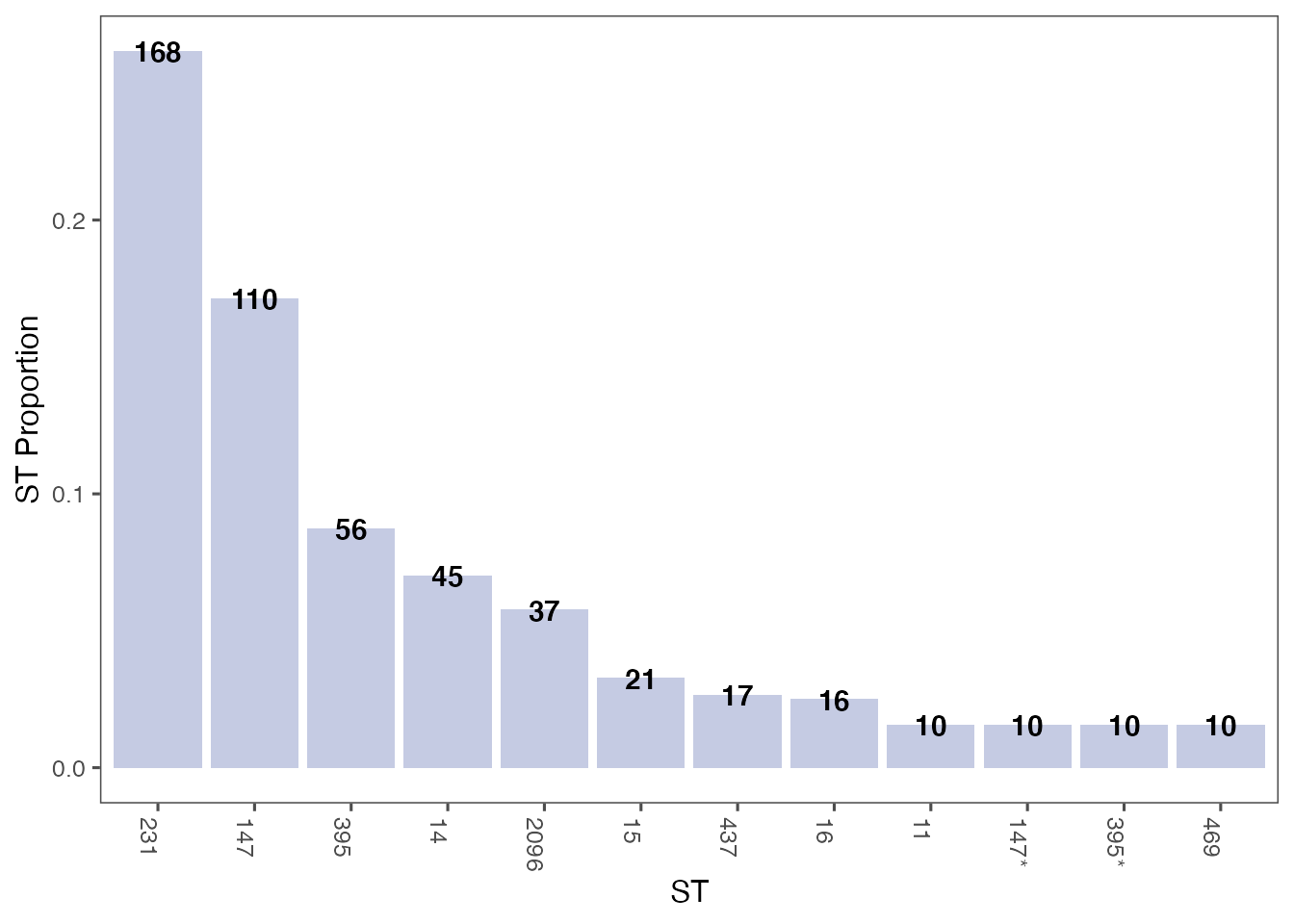
Plot most frequent STs by Sentinel Site
st_counts_by_sentinel_site <- count_sts_by_sentinel_site(combined_data)
most_frequent_st_counts_by_sentinel_site <- count_most_frequent_sts_per_sentinel_site(st_counts_by_sentinel_site, per_sentinel_site = 2)
plot_most_frequent_sentinel_site_sts(most_frequent_st_counts_by_sentinel_site)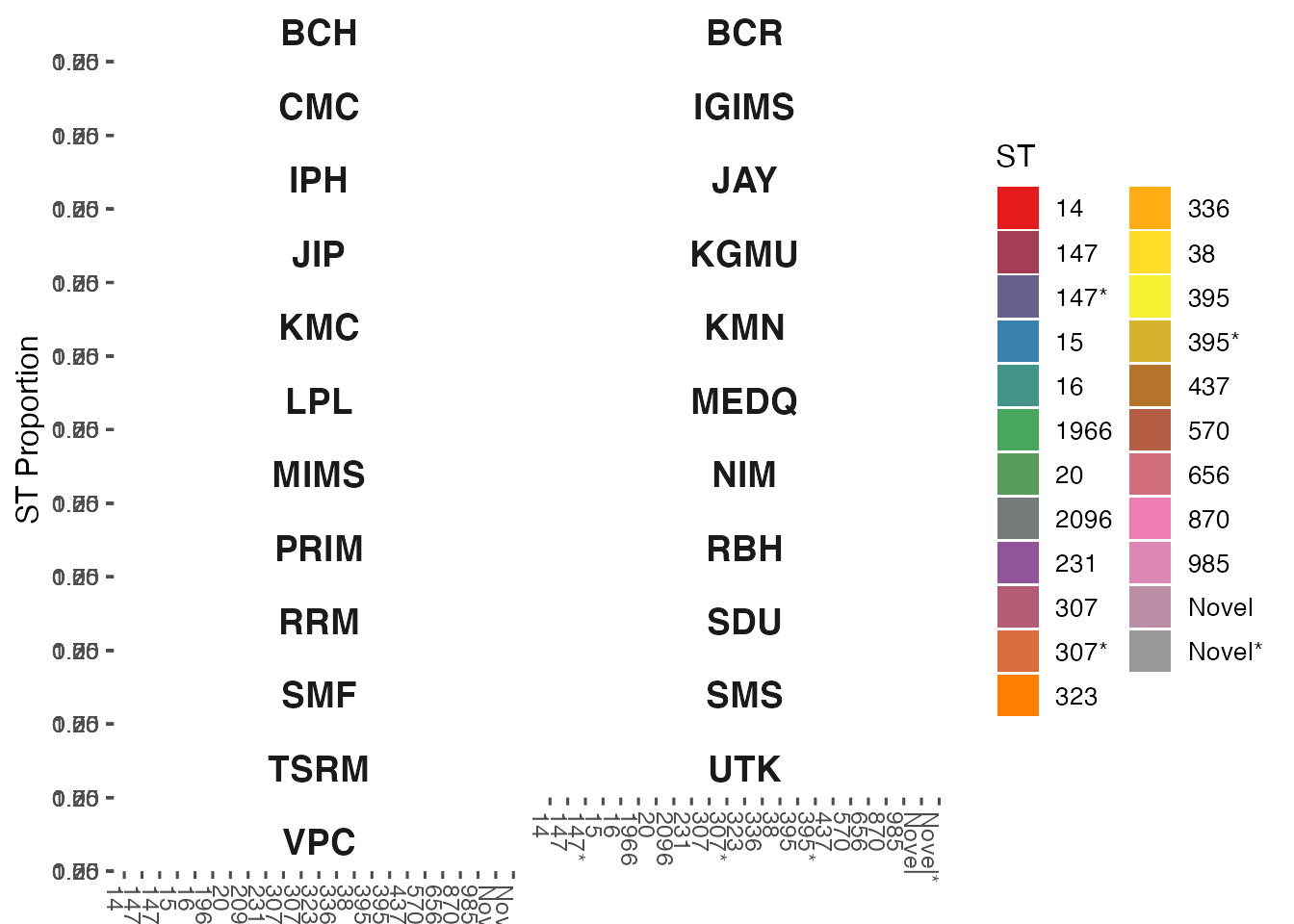
Plotting AMR data
First converting the amr data to long format and annotating with NCBI metadata and then plotting selected drug classes
# convert to long format
annotated_amr_data <- ghruR::annotate_amr_data(amr_data)
# filter data
annotated_amr_data <- ghruR::filter_long_data(annotated_amr_data)
# add Sentinel Site Code
annotated_amr_data %<>% left_join(
epi_data %>% select(`Sample id`, `Sentinel Site Code`),
by = 'Sample id'
)
# select drug classes
selected_drug_subclasses <- c("BETA-LACTAM", "CEPHALOSPORIN", "CARBAPENEM")
subclass_counts_by_sentinel_site <- ghruR::count_AMR_subclasses_by_sentinel_site(
annotated_amr_data,
samples_per_sentinel_site,
selected_drug_subclasses
)
amr_subclasses_plot <- ghruR::plot_AMR_subclasses_by_sentinel_site(subclass_counts_by_sentinel_site)Make a plot looking at the distribution of gene families. Combine them together
gene_family_counts_by_sentinel_site <- ghruR::count_gene_families_by_sentinel_site(
annotated_amr_data,
subclass_counts_by_sentinel_site,
selected_drug_subclasses)
gene_family_dot_plot <- ghruR::dot_plot_gene_family_counts_by_sentinel_site(gene_family_counts_by_sentinel_site)
cowplot::plot_grid(amr_subclasses_plot, gene_family_dot_plot,ncol =1, align="v", rel_heights = c(1, 3))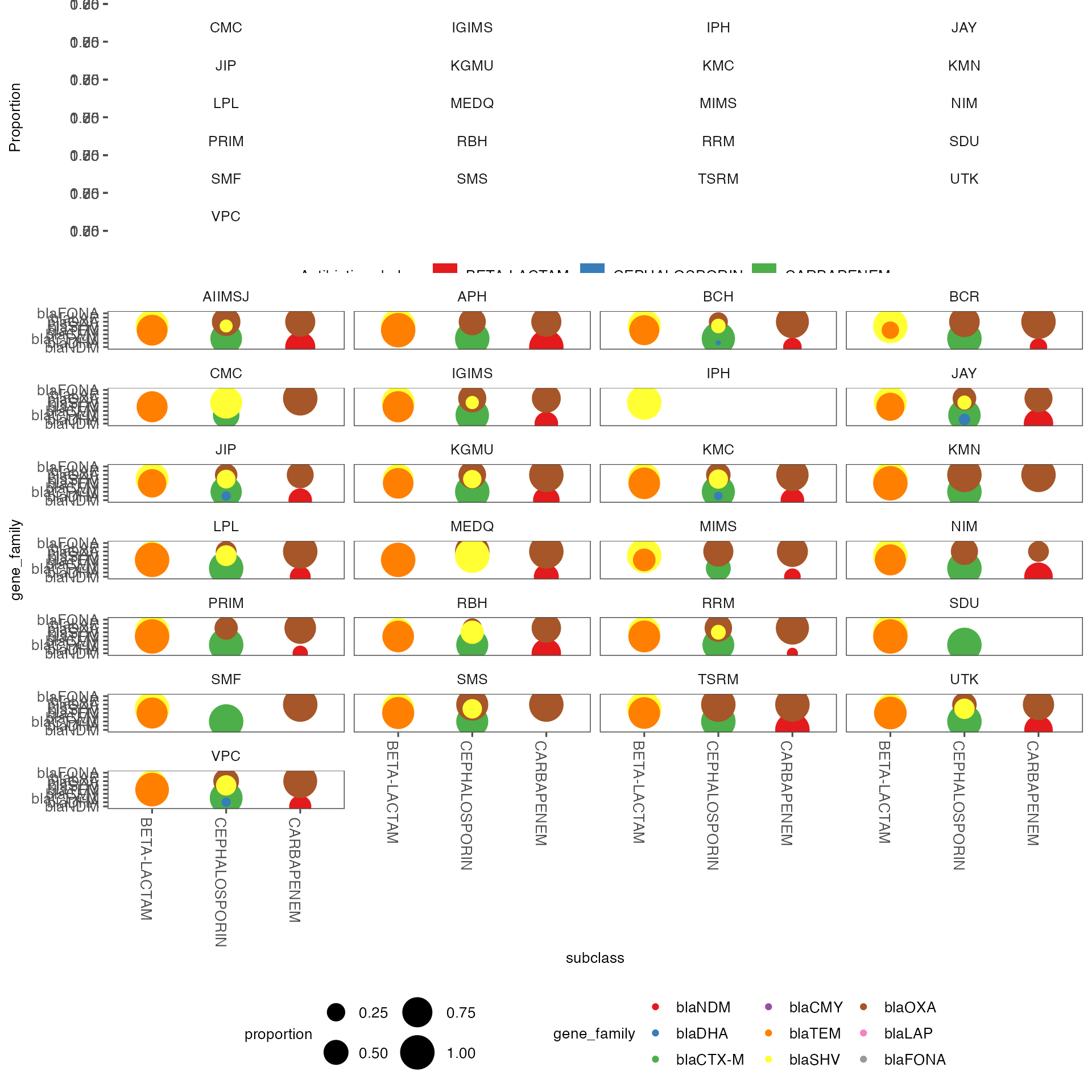 It is important to look at the gene alleles responsible for resistance. Here looking at just cephalosporin and carbapenem
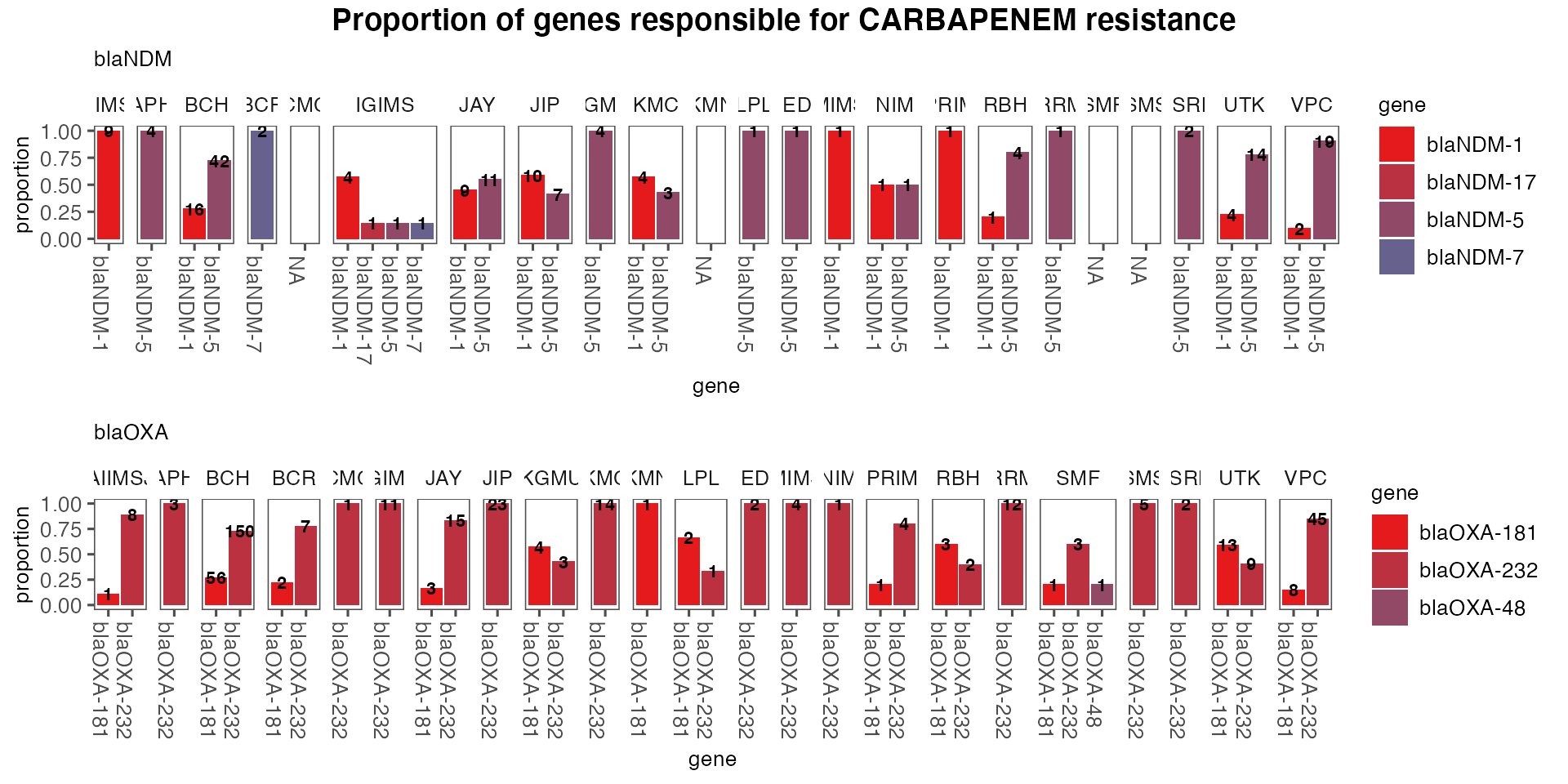
It is important to look at the gene alleles responsible for resistance. Here looking at just cephalosporin and carbapenem
drug_subclasses <- c('CEPHALOSPORIN', 'CARBAPENEM')
allele_counts_by_sentinel_site <- ghruR::count_alleles_by_sentinel_site(
annotated_amr_data,
gene_family_counts_by_sentinel_site,
drug_subclasses
)
allele_counts_plots <- ghruR::plot_allele_counts_by_sentinel_site(
allele_counts_by_sentinel_site,
drug_subclasses
)
print(allele_counts_plots[[1]])
print(allele_counts_plots[[2]])